Available courses

TH4022 Pentecostal Theology
This is a study of the origin and development of the Pentecostal Movement. This course examines the factors that led to the rise and spread of the Pentecostal Movement. This study will also examine distinctive elements of the Pentecostal Movement as well as departures from it. This study is designed to enable Pentecostal leaders to reflect on their heritage so as to recover the Pentecostal vision for reaching the lost world through the power of the Holy Spirit.
- Teacher: Dr. Victor Chanda

TH1033 Christology and Soteriology
This course is a thorough study of the Person and Nature of Christ. Included in it are His birth, life, perfect humanity as well as His true deity as revealed in the scriptures. Studied along with the doctrine of Christ is the doctrine of salvation through Christ alone. As a result this course is two part study. This course is designed to establish Christian leaders in their convictions that Jesus Christ is the only Saviour; He sanctifies, Heals, and is the soon coming king.
- Teacher: Dr. Victor Chanda

TH1013 Doctrinal Survey
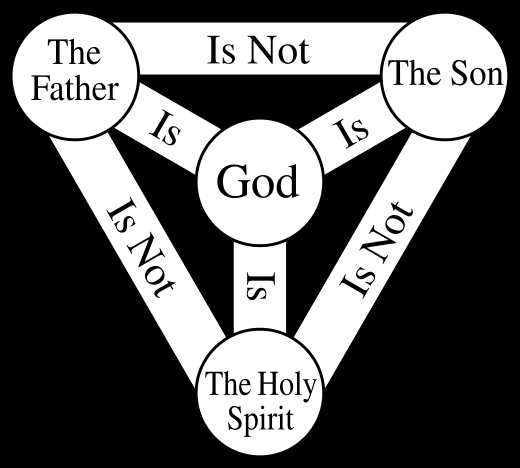 This is an introductory
course to systematic theology. It is designed to provide a study of basic Christian
doctrines. The thrust of this course is
to examine the doctrine of God (Theology proper) in detail as well as studying
the canon of the scriptures. This course is designed to establish Pentecostal
leaders in the doctrines of the Christian faith.
This is an introductory
course to systematic theology. It is designed to provide a study of basic Christian
doctrines. The thrust of this course is
to examine the doctrine of God (Theology proper) in detail as well as studying
the canon of the scriptures. This course is designed to establish Pentecostal
leaders in the doctrines of the Christian faith.
- Teacher: Victor Lukonsolo

JL Jan-Apr. 2024 Johannine Literature
The major New Testament literature which was authored by John, the beloved disciple, is the subject of this course. Our focus will be almost entirely on (1) the First epistle of John and (2) John’s Gospel. Time will be given to considering the unity and diversity of the New Testament as reflected in this literature, especially the fourth gospel; how it’s unique approach to the story of our Lord becomes, under the inspiration of the Holy Spirit, part of the unified message of the four gospels.
- Teacher: Dr. John Kerr

CCC Jan-Apr. 2024 Cross Culture Com
COURSE DESCRIPTION:
“Many leaders of the world believe that only through successful cross-cultural communication will mankind and society survive. Because of the vast improvement in transportation and technology in the last few decades, the world is indeed becoming a global village. However, man’s ability to communicate well with his once distant neighbours has not kept pace. The increasing contact between peoples who are culturally different is a major problem. Human communication between members of the same race, community, and even the same family is very difficult. How much more does communication between different kinds of people demand much attention and effort” (Del Tarr, 1996).
This course attempts to help the student who would become a ‘sent one’ to present Christ and His kingdom in his own environment and in other cultures. To do this, we address the nature of communication, the relationship of communication and culture, how to reach people where they are, how different people think and express ideas across cultures and subcultures within a culture, and how the thought and expression of people affect their behaviour.
- Teacher: Ruth Kerr

- Teacher: Dr Mumba Gabriel
- Teacher: Chibangu Kolala
- Teacher: Victor Lukonsolo

ED4022 Curriculum Development
The aim of the course is to provide candidates with an opportunity to deepen their conceptual understanding of the educational and curriculum issues and relate the principles to their professional experiences. This ability to relate theory and practice will enhance their analytical capacities. The students will be assisted to appreciate the interrelationships between the theories and actual practices.
- Teacher: Alice Chiwasa

MT3113 Analytical Geometry & Calculus
This course will bring out the historical and epistemological development of analytic geometry and vector calculus. It will cover the survey of actual situation and historical background of teaching of analytical geometry and vector calculus.
- Teacher: Phillip Mubanga

EN 2124 Syntax in English Language
This course is aimed at familiarizing learners with the basic goals and assumptions of Generative Grammar, training students in the rudiments of syntactic analysis and syntactic theorizing and argumentation, and acquainting students with the major syntactic structures of English and their relevance to linguistics.
- Teacher: Chibangu Kolala

EN 3124 Semantics of the English Language
This course addresses the semantics of singular and plural nominals in English language that manifest a binary morphological number distinction within this category. It shall develop an analysis which treats the plural morphemes as semantically relevant. the competition between singular and plural nominal will be grounded in bidirectional optimization form-meaning pairs.
- Teacher: Silvia Kapasa

MT3123 Integral & Differential Calculus
This course is aimed at developing thinking, reasoning, communication and modeling skills through mathematical approach to problem solving. Students will appreciate the value of mathematics in making informed decisions in life. They will acquire vigorous habits of mind through mathematical problem solving, and use of mathematical models
- Teacher: Phillip Mubanga

CV4113 Constitution & Human Rights: Public Policy & Legal Education Study
This course will focus on the meaning of constitution and constitutional government. It shall discuss the supremacy and legitimacy of the constitution. The course will further discuss the meaning and importance of Human Rights to people in the society. It shall endeavor to discuss the development of human rights, principles of human rights, composition of human rights, characteristic of human rights, categories of human rights. It shall also discuss the various organisations which support human rights.
- Teacher: Tamala Mbewe

RS2013 African Traditional Religion: Indigenous Religions in Central Africa
The course aims at bringing the use of linguistic analysis to uncover early religious history. It will identify stages of Eastern and Western Bantu expansion history. The course shall compare and contrast the European witchcraft with the African witchcraft. It shall also account for the social and political significance of the rain shrines.
- Teacher: Kashiwa Mumbi

TH702 Apologetics
TRANS-AFRICA CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY SYLLABUS
COURSE: APOLOGETICS - MASTERS LEVEL DATE: JANUARY, 2021
INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Richard K. BALL LEVEL: MATS
____________________________________________________________________
COURSE DESCRIPTION (SCROLL DOWN TO READ THE ENTIRE DESCRIPTION):
This is a curated, self-study course in Christian apologetics with emphasis on critical issues and practical approaches in the African context.
Apologetics is the defense of the Christian faith. Broadly speaking there are two streams of apologetics instruction, reflecting the two dominant ways of viewing Christian apologetics. The first is philosophical/academic. This covers such topics as the history of apologetics, natural theology, philosophical proofs for the existence of God, the rules of Logic, and the issue of theodicy — the justice of God.
The second view apologetics as an on-the-ground defense against competing religions and ideologies as well as Christian heresies, cults, and unbalanced teachings, e.g., the prosperity gospel.
This course will focus on the second view while covering the first depending upon student interest.
COURSE OBJECTIVES and OUTCOMES:
At the end of this course the student should be able to:
- Identify and discuss major areas of Christian apologetics: e.g., faith vs. reason; the Bible vs. science; theodicy; the existence of God; the person of Christ; world-views; other religions/cults.
- Identify and use available internet resources for engaging in practical apologetics.
- Identify and address threats within -- cults, heresies; and threats from without -- other religions and ideologies, including, e.g., scientism which is the belief that science is the basis of all knowledge.
- Apply to an African context.
COURSE FORMAT AND ASSETS:
This is a curated, self-study, online course with an emphasis on group participation and mutual support. The course will make use of TACU online teaching resources (e.g., Moodle) and the Trans-Africa public Facebook apologetics site. A copy of the instructor's Keynote slides will be made available.
COURSE OUTLINE and SCHEDULE:
COURSE ASSESSMENT:
|
ASSESSMENT |
DUE DATE |
% |
|
CLASS ASSIGNMENTS - WEEKLY JAN-FEB |
January-Feb |
60% |
|
Research Paper/Assignment |
April 1 |
20% |
|
Overall Contribution to the Class, including participation in discussions led by others |
|
20% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL |
|
100% |
TEXTS and RESOURCES:
Internet-accessible, and/or files made available via Moodle and as assigned by the instructor.
Apologetics videos, e.g., William Lane Craig
Apologetics e-books, e.g., Mere Christianity
Apologetics websites, e.g., Apologetics315
Apologetics courses, e.g., C.S. Lewis Institute
Apologetics ministries, e.g., AC/FAR
METHOD OF INSTRUCTION:
Students will engage with the course material via a variety of methods: reading, both books, articles and websties; locating and viewing internet videos from e.g., Youtube; participation in discussion over the readings and viewings; participating in presentations by both the instructor and other students; conducting independent research, and developing a plan that synthesizes and applies the course content.
GRADING EXPECTATIONS:
- Academic integrity including timely submission of assignments and avoidance of illegitimate appropriation and use of others’ work, but rather, demonstrating appropriate and gracious acknowledgment of sources used
- Lively participation and contributions to public class assignments (e.g, posting to the TACU Apologetics website).
- Critical thinking and personal conclusions
- Structuring and presentation of clear arguments with supporting data and rationale
- Depth and accuracy of research
- Creativity in written and verbal presentations
- Graduate-level research and writing skills
OVERALL GRADE “10”. Work exceeds expectations. Student demonstrates excellent and exceptional knowledge of the subject. Able to synthesise, critically assess and apply the complex concepts. Student is prepared to elaborate on/discuss subtle and deeper aspects of the topic. He/she demonstrates insights, originality and creativity. There is evidence of independent reading beyond the core texts. This student has excellent preparation for further studies.
OVERALL GRADE “9”. Student demonstrates high standards of knowledge. Work meets all expectations. Good comprehension of the material. Student is able to analyse and critically evaluate the material and is able to transfer knowledge to other areas. He/she has very good preparation for further studies.
OVERALL GRADE ‘8’. Student demonstrates good knowledge of the subject and ability to summarise well. Shows good and sound comprehension of concepts and ability to evaluate and use them. Work meets all expectations but has insignificant weaknesses. Good preparation for further studies.
OVERALL GRADE “7”. Student demonstrates core knowledge of the subject but does not show complete understanding. Shows good comprehension of core texts, principles and concepts, but has limited ability to critically evaluate and use them. Shows adequate ability to develop arguments and present them. Satisfactory preparation for further studies.
OVERALL GRADE “6”. Student demonstrates reasonable core knowledge of the subject. Shows limited comprehension of core texts and principles but very little ability to critique or evaluate them. Shows evidence of having read core material but work lacks depth of analysis.
The instructor reserves the right to adjust the final course grade of any student by up to one letter grade, higher or lower, to better reflect the student’s performance, improvement, learning differences, and effort/participation in this course.
ACADEMIC DISHONESTY and PLAGIARISM:
In an instructional setting, plagiarism occurs when a person presents or turns in work that includes someone else’s ideas, language, or other (not common knowledge) material without giving appropriate credit to the source.
Plagiarism will not be tolerated, will result in a failed grade on an assignment, and may result in failing this course.
Academic dishonesty constitutes a serious violation of academic integrity and scholarship standards that can result in substantial penalties, at the sole discretion of the University, including but not limited to, denial of credit in a course as well as dismissal from the University. In short, a student violates academic integrity when he or she claims credit for any work not his or her own (words, ideas, answers, data, etc.) or when a student misrepresents any academic performance.
PROFESSOR CONTACTS:
Dr. Rick Ball
Email: rkballtyndale@gmail.com
- Teacher: Richard Ball
Skip site announcements
